Stepping up to the plate.
With the events of the past few months, we all have had to make adjustments, both in our family life and work environments. So I thought a bit of uplifting news would be appropriate to help kick off this issue.
As a manufacturing company, proceeding as normal with day-to-day fulfillment of customers’ orders, we were able to tap into our capabilities, and do our part to help where needed…we listened, and we came together! Proudly, to this date, we have manufactured and donated 1,870 (PPE) medically approved face shields to front-line health workers. As a productive and hard-working company, we can truly say to each other, “Great teamwork!”
Stay safe and enjoy the content below, especially the comic strip…it may relate to most of us!
Sylvia Flegg, Marketing Manager
All power plants are created with one particular goal: to produce electric power as efficiently as possible.
How do power plants work?
Electrical power starts at the power plant. In most cases, a power plant consists of an electric generator. Something has to spin that generator — it might be a water wheel in a hydroelectric dam, a large diesel engine or a gas turbine. But in most cases, the object spinning the generator is a steam turbine. The steam might be created by burning coal (as shown in diagram below), oil or natural gas.
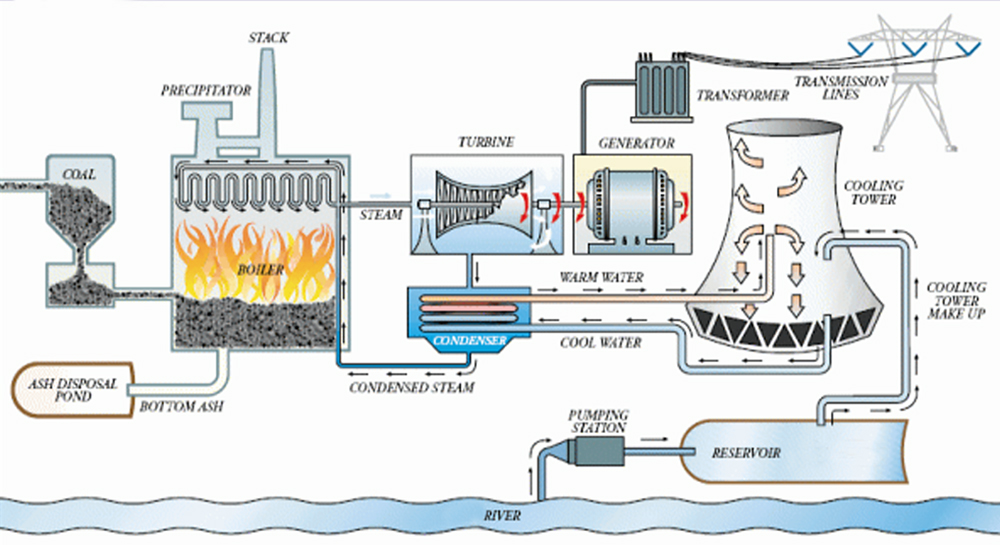
How do power plants generate electricity?
Electricity is a secondary energy source, which means that electricity is obtained from the conversion of other primary sources of energy, such as coal, natural gas, nuclear, solar, or wind energy. The power plant is the location in which the energy conversions take place.
Power plant generator
The power plant generator is a device that converts mechanical energy obtained from an external source into electrical energy as the output. It is important to understand that a generator does not actually ‘create’ electrical energy. It uses the mechanical energy supplied to it to force the movement of electric charges present in the wire of its windings through an external electric circuit.
Power generation equipment
In each plant, the following basic power generation equipment is present:
Heat source: Provides heat to generate steam.
Turbine/generator: Uses the energy of the steam to turn a turbine/generator that produces electricity.
Condenser: Condenses the steam back to water so that it can be returned to the heat source to be heated again.
Pump: Provides the force to circulate the water through the system.

Types of power plants
Thermal power plants use fuel to heat up water from a reservoir, which generates steam (usually at a high pressure). The highly pressurized steam then travels through pipes to rotate the fan-like blades of a turbine. As the turbine begins to spin, it causes giant wire coils inside the generator to turn. This creates relative motion between a coil of wire and a magnet, which pushes electrons and starts the flow of electricity.
Fossil fuel power plants burn their fuel in order to create the thermal energy to run their external heat engines. A simple cycle gas plant does not use steam like the others: it works similar to a jet engine where natural gas is ignited and burned and the heat creates pressure that turns the turbine. Combined cycle gas plants use both the heat and steam as well. Types of fossil fuel plants include coal-fired power plants and natural gas power plants—accounting for the largest producers of electricity around the world (see data visualization below).
Transportation of electricity
Once electricity is generated, transformers “step-up” the electric power to a higher voltage in order to travel long distances with minimal energy loss. It then travels through “pylons” along overhead power cables to its destination, where transformers subsequently “step-down” the electric power to safe voltages for houses and utilities.
Durlon® Durtec®
Durlon Durtec gaskets are made with a specially engineered machined metal core that is bonded on both sides with soft covering layers, typically flexible graphite. The core is produced by proprietary technology that allows the finished gasket to have the best possible mechanical support function. The Durtec core is virtually un-crushable unlike conventional corrugated metal core gaskets. The precision construction guarantees that Durlon Durtec gaskets will have excellent sealing characteristics even under low bolt loads.
The Durtec gasket is designed to withstand high temperatures and pressures, to be blowout resistant, to be fire safe, and to resist toxic and or corrosive chemicals for such applications as: pipeline flanges, valves, small & large pressure vessels, heat exchangers, towers and tanks.
Composition:
The Durlon Durtec Gaskets made with a specially engineered metal core technology that is bonded on both sides with soft covering layers, typically oxygen-inhibited flexible graphite or Durlon 9600 ePTFE facing. The core is produced by proprietary technology that allows the finished gasket to have the best possible mechanical support function. Corrugations in Durlon Durtec are virtually uncrushable unlike conventional corrugated metal core gaskets. The precision construction guarantees that Durlon Durtec gaskets will have excellent sealing characteristics even under low bolt loads. The Durlon Durtec with ePTFE (Durlon 9600) Facing – Able to withstand the demands of high vibration, aggressive chemicals and cyclic conditions – Suitable for use in pulp & paper applications and as a replacement for low stress spiral wound gaskets – Conforms well to damaged flange faces.
Download the Durlon® Durtec® Tech Sheet.

Answer:
Proper Gasket Installation will increase the LIFE of the gasket, reduce LEAKAGE and can lower your MAINTENANCE costs.
The Fluid Sealing Association
Founded in 1933, the FSA is an international trade association. Member companies are involved in the production and marketing of a wide range of fluid sealing devices primarily targeted to the industrial market. FSA members account for a majority of the manufacturing capacity for fluid sealing devices in the Americas market.
Learn about membership.
The FSA offers many technical publications written by experienced and knowledgeable members.
Are you looking for Specifications and Recommended Practices for various media and applications? The Fluid Sealing Association offers complimentary documentation here.
Welcome to the Fluid Sealing Association KnowledgeBase!
The FSA KnowledgeBase is a source of highly reliable technical information regarding seals and sealing systems – and is FREE to all who wish to set up a complimentary account. Learn more here.
Industry Tradeshows
See next issue for up-coming events
Next issue highlights: Industry and product focus. We’ll share a new video, news and upcoming trade shows that you may want to look into. And of course, we will put those genius brains to the work again and tickle your funny bone with another adventure from our gasket guru. See you in August 2020!







